US inflation rose to 3.0% year-on-year in September, and futures markets are still pricing in a Federal Reserve rate cut next week.
The overall CPI was 3.0% year-over-year and 0.3% month-over-month, while the core CPI remained at 3.0% year-over-year and 0.2% month-over-month. Gasoline prices rose 4.1% month-over-month, and home price inflation remained at around 3.6%. The Bureau of Labor Statistics released cost-of-living data according to the schedule set by the Social Security Administration, despite the lockdown.
CME Group's FedWatch analytical database shows a 90% chance of a 25 basis point rate hike at the October 29 FOMC meeting, raising the target from 3.75% to 4.00% today to 3.50% to 3.75%.
Beyond the immediate meeting, the same FedWatch distribution places the center of the trajectory around 3% by this time next year.
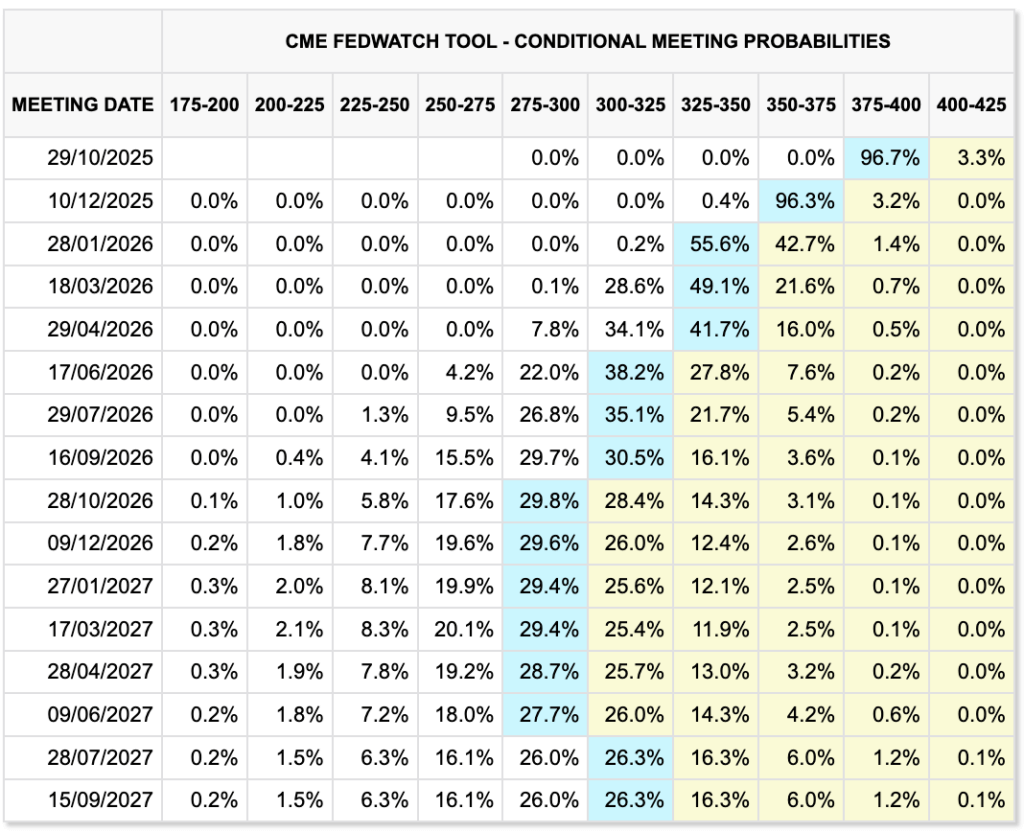
For the October 28, 2026 meeting, the highest probabilities lie in the range of 2.75% to 3.25%, with small "tails" on either side.
The simple probability-weighted average of this distribution is about 2.97%, corresponding to a decline from current levels to about 3% over the next year.
| Target Range (%, October 28, 2026) | Probability |
|---|---|
| 2.50–2.75 | 17.6% |
| 2.75–3.00 | 29.8% |
| 3.00–3.25 | 28.4% |
| 3.25–3.50 | 14.3% |
| Other trash bins | 9.9% |
Street maps and rules-based estimates provide a useful tool for cross-checking. Goldman Sachs expects three cuts in 2025 and two more in 2026, bringing the funds rate to a range of 3.00% to 3.25% by the end of 2026.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland's "Simple Monetary Policy Rules" dashboard shows a median policy path ranging from 3% to 10% for 2026, depending on the forecast, as a reminder that sticky inflation components could keep interest rates above the implied futures rate. The gap between futures rates and the policy creates a hawkish risk to the final 3% level if core disinflation stalls.
The context of the curve helps determine the extent to which monetary easing will impact financial conditions.
The two-year yield is hovering around the midpoint of the 3.4-3.5% range, and the 10-year yield is around 4%, while the 30-year breakeven inflation rate is close to 2.25%.
A Reuters survey of strategists points to a longer-term dynamic that will remain stable at 4.1-4.2% over the next six to 12 months as term premiums decline and fiscal supply tightens.
If the final outcome remains unchanged but the initial outcome falls, the curve will steepen, which will affect how "loose" overall financial conditions can become as policy is cut.
In digital assets, the connection to politics is now evident in both real returns and fund flows. According to CoinShares, in early October, global cryptocurrency exchange-traded fund (ETP) exchanges saw a record weekly inflow of $5.95 billion as Bitcoin reached a new high of around $126,000. The following week, outflows, primarily Bitcoin, of around $946 million followed amid heightened volatility. We also saw liquidations of over $19 billion after US President Donald Trump upended macroeconomic forecasts by announcing new tariffs on China.
Spot Bitcoin consolidated between $108,000 and $111,000 during the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Federal Reserve (FOMC) releases. These flow impulses influence how macroeconomic impulses affect the price, as ETF demand now accounts for a significant portion of the increase in purchases.
In the short term, a 25 basis point cut, coupled with cautious forecasts, will likely weaken the 10-year rate, while the 10-year rate remains stable at around 4%. If the dot chart and statement pave the way for a December move, the easing of the 10-year rate will become more apparent, and the dollar may weaken slightly.
If the Committee backs down and real rates rise instead, risk assets typically recover until new data changes the trajectory.
The combined CPI numbers give the Fed room to continue moving toward its first rate cut, as gasoline was the main driver of the monthly rise, and a correction in retail prices in October or November will help the fundamentals align with the story of gradual disinflation.
Looking ahead to October 2026, three distribution paths can be identified, as implied by future events and rules.
The slow disinflation baseline scenario maintains a downward trend in core inflation without a labor market shock, the policy rate fluctuates around 2.75–3.25%, and real yields decline as underlying inflation declines.
Stubborn inflation keeps the policy rate near or above 3%, the Fed leans more cautiously, and the funds rate stabilizes closer to 3.25%-3.75% amid a stronger dollar and periodic tightening of financial conditions, consistent with the Cleveland Rules bias.
The scary growth path envisages an initial easing to 2.25%-2.75% and a weaker dollar after the initial risk-off phase.
In all cases, Bitcoin's beta relative to real returns remains central, with the ETF flow channel adding convexity as conditions soften.
| The Path to October 2026 | Interest rate range | Macromarkers | reading BTC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sliding and disinflation | 2.75%–3.25% | The core cools gradually, about 4.0%–4.2% per 10 years | Constructive bullishness if real yields decline and ETF inflows persist |
| Sticky inflation | 3.25%–3.75% | Core about 3%+, breakeven stable | Limited range with a strong US dollar and higher real rates |
| Fear of growth | 2.25%–2.75% | Unemployment is rising, the ISM index is below 50 | Two-stage recovery: risk aversion followed by liquidity-led recovery |
Global headwinds are maintaining the balance. The ECB suspended rate cuts at the beginning of 2025, and major banks do not expect further cuts in 2025, limiting the dollar's decline under the euro's influence.
The Bank of England is easing monetary policy more cautiously as inflation in the UK remains above target. In the US, the Chicago Fed National Financial Conditions Index and the 10-year TIPS yield, tracked by FRED, remain useful indicators of Bitcoin's macroeconomic beta.
The FOMC decision next week will be the catalyst in the near term. Futures show a 25 basis point rate cut is priced in, with the market's implied cap at approximately 3% by October 2026.
Source: Сrypto Orda

